Roger Clarke's Web-Site
© Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 1995-2024

Infrastructure
& Privacy
Matilda
Roger Clarke's Web-Site© Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 1995-2024 |

|
|||||
| HOME | eBusiness |
Information Infrastructure |
Dataveillance & Privacy |
Identity Matters | Other Topics | |
| What's New |
Waltzing Matilda | Advanced Site-Search | ||||
Revised Version of 14 November 2018
This supersedes http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/RTF-180430.html
© Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 2017-18
Available under an AEShareNet ![]() licence or a Creative
Commons
licence or a Creative
Commons  licence.
licence.
This document is at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/RTF.html
The term 'RegTech' emerged in 2015 to refer to technologies supporting regulatory processes. Its initial usage was limited to compliance aspects within financial services corporations. This paper instead adopts a literal interpretation of the term and articulates a broader vision of information technology applied to regulation. It argues that RegTech is needed in all sectors, and by all participants in the regulatory game. A framework is presented which comprises models of the regulatory space, regulatory layers, regulatory players and regulatory play. This is demonstrated to enable the identification of opportunities for IS practice and IS research, and the conception of more effective and better integrated support for the business functions of regulators, of regulatees, and of the beneficiaries of regulation.
The term 'RegTech' has recently emerged as a means of referring to the use of technology in support of regulatory activities. It appears to have been first used in this sense in a UK Government report on financial technologies in March 2015 (UKGOS 2015). The earliest occurrence found using Google News was a single, fleeting mention in an article on the UK Budget (Glick 2015). The earliest mentions found by Google Scholar are Arner et al. (2015) and Treleaven (2015). The contraction derives directly from the use by software marketers of the term 'FinTech' to refer to technologies applied within the financial services sector, particularly those that are perceived to be disruptive or potentially profitable. The motivation for projection of the term RegTech was the desire for "regulatory reporting and analytics infrastructure ... typically to improve efficiency and transparency [in financial regulation]" (UKGOS 2015, pp.12, 47).
The RegTech notion was very quickly co-opted by the financial services industry association, the Institute of International Finance, without attribution (IIF 2015). IIF adopted a narrow definition of "the use of new technologies to solve regulatory and compliance requirements [in the financial services sector] more effectively and efficiently" (IIF 2016, p.2). A slightly different but also narrow approach was adopted by the UK Financial Conduct Authority: "RegTech is a sub-set of FinTech that focuses on technologies that may facilitate the delivery of regulatory requirements more efficiently and effectively than existing capabilities" (FCA 2016, p.3). Academic papers on the topic have generally adopted these definitions as their starting-point (e.g. Arner et al. 2015, Daly & Butler 2018, Anagnostopoulos 2018).
Technology providers, eager to make their offerings attractive to corporations, have grasped the opportunity, formed new associations, and 'talked-up' the market. The financial services sector is naturally a primary target because it is subject to very substantial formal regulation. These imposts derive from two sources. One is the enormous economic and social costs arising from the spectacular failure of softer regulatory forms, resulting in financial crises (RBA 2014). The other factor is substantial and frequently-changing interventions by law enforcement and national security agencies. These mandate the provision of data about transaction flows and impose onerous requirements on processes for the identification and identity authentication of the sector's customers. These demands were justified originally by the spectres of organised crime, then drug lords and arms traders, and since 2001 terrorism (Zagaris 2004, Gilmore 2004).
Industry documents and the early academic literature alike emphasise contemporary excitement technologies, such as blockchain, Big Data, predictive analytics, biometrics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning and the Internet of Things (IoT) (Arner et al. 2016, Baxter 2016). Such technologies may well have something to offer, despite the massive and in part seriously misleading hype associated with them (Clarke 2016a). On the other hand, even without resorting to 'vogue but vague' technologies, a great many opportunities exist for RegTech initiatives. Technology providers naturally 'follow the money' and focus on large corporations that have substantial obligations imposed on them by formal regulatory instruments, and hence need to perform onerous compliance activities. The financial services industry has accordingly been the initial focus, and will inevitably remain an important one. RegTech's scope is, however, far wider than that. Other industry sectors are subject to formalised regulatory requirements, and many looser and less stringent business processes can also benefit from technological support.
Regulatory arrangements are important wherever natural controls fail to curb excesses. This paper contends that, particularly in view of the scale of contemporary economies and societies, technologies need to be harnessed in support of activities of all participants in regulatory processes. This paper conceptualises the central concept in this paper as follows:
RegTech is technological applications in support of the activities of regulators, regulatees, and entities that are intended to be beneficiaries of regulatory activities
RegTech is relevant to IS executives and practitioners for two reasons. All regulatory regimes impose requirements on IS; and all regulatory regimes themselves depend on IS to support their operation. Because regulatory factors are intrinsic to IS, this paper is in part concerned with IS heartland, and should be of interest to readers generally. However, the paper is also in part concerned with an applications area which, like for example ERP, CRM, eHealth and GIS, is of specific interest to only a sub-set of the IS profession and of IS academics. The body of the paper develops arguments that show that research into regulatory applications is legitimate, desirable, feasible for a proportion of IS professionals and academics, and, using the framework that I present, capable of being undertaken in a manner that will deliver payback, both practical and theoretical.
The paper commences with a review of the IS literature in relation to regulation. This concludes that the area has attracted only a modest amount of attention. The paper accordingly addresses the question of how IS practitioners and academics can make good that shortfall, grasp opportunities available to them, and serve inadequately-filled needs of organisations, the economy and society. On the basis of regulatory theory, a framework is presented, comprising four inter-related models of regulatory institutions and processes. The framework is shown to enable the identification of opportunities for the creation of new IS and the adaptation of existing IS. The breadth of opportunities is complemented by consideration of the specific applications area of drones. Implications are drawn for practice and research.
To what extent has regulation attracted the attention of IS researchers? A preliminary study was undertaken, in late 2017, of the IS literature concerning RegTech and regulation more generally. It was repeated in late 2018. Searches were undertaken in a variety of indexes, including both those with a broad catchment-area and IS and IS-cognate indexes. Papers found in this way were inspected for further relevant papers, and citations for key papers were checked.
Commercial indexes such as Web of Science and Elsevier continue to have narrow catchment areas, particularly from the perspective of IS. Google Scholar represents a more valuable, broad-scan tool because of its very liberal catchment, and despite its limited search flexibility and inappropriate-for-research precedence algorithm. The AIS eLibrary is of course the most relevant targeted collection. The orientation of the ACM, IEEE and IET libraries is naturally strongly towards technical topics, and hence only a very small proportion is of relevance to regulation. The various indexes offer very different search-functionality and -interfaces, and achieving suitable balance between over- and under-inclusiveness of search results requires considerable familiarity with each of them.
Searches commenced with the specific search-term <RegTech AND "information systems">. Given the recency of the term's emergence, and the substantial delays inherent in research conception, conduct, reporting and publication, it is unsurprising that RegTech was yet to make its mark. For example, in late 2017, Google Scholar returned only 40 hits, of which few were relevant and only 2 were in the formal IS literature. The AIS eLibrary's collection of c. 37,000 articles, searching on <RegTech>, yielded 4 hits in late 2017 and 8 in late 2018, although only 2 of them were peer-reviewed. In most cases, the term gets little more than a mention, but two papers propose particular forms of RegTech (Moyano & Ross 2017, Huang & Chiang 2017). Even in late 2018, most of the Basket of 8 journals returned no hits for <RegTech>, with only 3 papers found, in 2 journals.
The application of technology in support of regulation of course started long before the term 'RegTech' was coined. However, even when further searches are undertaken using variants of <regulat* AND "information systems">, still only relatively small numbers of articles relevant to this study came to light. The paucity of research on regulation in IS contexts has been previously noted (Eggert et al. 2013). In the Introduction to a Special Issue on FinTech, Alt et al. (2018) comment that "a brief analysis undertaken on Google Scholar confirmed the impression of only limited available research in the RegTech domain. This is remarkable since legal and regulatory requirements and checks have accrued in view of the growing regulation that has occurred in the financial industry after the financial crisis of 2008".
Utilising the search-term <regulatory OR regulation OR compliance> within the AIS eLibrary, 60 articles were located with a relevant term in the title, and 261 in the abstract. This compares with 335 in the abstract for health, 271 for ERP, and 174 for <GIS OR geographic>. However, many of the articles identified in this way are concerned with matters outside the scope of this article, such as personal self-regulation, regulatory focus theory, and organisations' internal governance mechanisms including compliance by staff with IT security policies. The distribution over the period 1995-2018 was close to rectangular, and hence there was no evidence of a surge of publications since the emergence of the RegTech notion. In the archives of the 'Basket of 8' IS journals, among the c. 8,000 articles published to date, strings such as <regulat*> were found in 25 titles and 70 abstracts. Google Scholar finds hundreds of papers, but only a small proportion of the sources located were of direct relevance to this study.
In all, the literature research generated 40 relevant articles in IS or cognate journals (of which 24 are in Basket of 8 journals), and a further 20 in IS conferences, and the list of authors includes over a dozen highly-cited IS academics. A further indicator of the relevance of the topic was that the number of individuals in the AIS Faculty Directory who nominate regulation as an interest is considerably greater than the numbers for, for example, the busy application areas of health and geographic information systems.
The relevant papers encompass a wide array of specific topics, primarily in relation to compliance within the financial services sector, and privacy. Few major works were found, such as systematic literature reviews - but see Cleven & Winter (2009), Akhigbe et al. (2015) and Hashmi et al. (2018) - and proposed research agendas - but see Coglianese (2004), Abdullah et al. (2010), Cousins & Varshney (2014) and Akhigbe et al. (2017). Few of the relevant works are highly-cited, the largest Google citation-counts being c.70 for Coglianese (2004) and Abdullah et al. (2010), c.40 for Duncombe & Heeks (2003), and c.25 for Cleven & Winter (2009).
No papers at all were found that adopted the perspective of individuals and organisations that are intended to be the beneficiaries of regulatory regimes. A modest number have the design of regulatory measures as the central focus (Neo 1992, Clarke & Jenkins 1993, Williams 1994, 1996, Hosein & Whitley 2002, Knackstedt et al. 2013), while some at least acknowledge that regulators have a perspective different from those of regulatees (e.g. Gomber et al. 2018).
Because most of the published research has been specifically from the perspective of regulatees, the primary focus has been on compliance and the limitation of damage to regulatees' interests. Some papers are concerned with operational aspects of IS, in particular the influence of regulatory measures on IT applications and their use (Mlcakova & Whitley 2004). Others study regulatory regimes' impacts on system design (El Kharbili 2012, Knackstedt et al. 2014), on business process management (Schultz 2013, Fellman & Zasada 2014, Sadiq & Governatori 2015), and on shared infrastructure (Reimers et al. 2015). Smith et al. (2010) and Gozman & Currie (2014) studied difficulties in achieving compliance, and Clemons & Madhani (2010) considered circumstances in which new business models overwhelm existing regulatory mechanisms.
Regulation's strategic impacts were recognised even during the early years of strategic IS research, although it was originally regarded almost exclusively as a constraint rather than as an opportunity. Among the 14 considerations in the 'Organizational Strategy Set' of King (1978) was "organization must be responsive to regulatory agencies", and Farbey et al. (1995) referred to "regulatory or legal necessity" (p.42). See also Fisher & Harindranath (2004) and Greenaway et al. (2015). Some studies have extended beyond compliance with regulation to also consider its subversion (Henry et al. 2007).
However, impacts of regulatory regimes on strategic IS can be not only significant, but also positive or enabling (Knackstedt et al. 2013). One example is where regulatory measures provide comfort to the individuals and organisations that buy products and use services. This contribution to trust arises from the feeling that the buyer's risks are reduced, and that recourse is available when things go wrong (Clarke 2001b, Tang et al. 2008, Tsatsou et al. 2010, Xu et al. 2012, Wall et al. 2016). The aura can be sustained by a mixture of careful handling of issues as they arise and management of media and government relations. Further, to the extent that regulators take enforcement actions against corporations that fail to fulfil their compliance obligations, the impact of maverick competitors can be reduced, and the positive image associated with mainstream providers can be enhanced.
Regulatory measures can create or strengthen barriers to entry by competitors (Klapper et al. 2006, Lane & Koronios 2001), and can increase barriers to exit by customers. A common example is obligations on financial institutions in many countries, including the USA, UK, Canada and Australia, to 'Know Your Customer', i.e. to gather a considerable amount of data about the person or organisation, and to conduct identity authentication processes. These represent a barrier to entry in that new providers have to invest considerable time and money on compliance, as a condition of doing business. Users of these companies' services are confronted by onerous and time-consuming documentary requirements in order to establish a relationship with each alternative or additional provider, and these high switching costs naturally reduce customer churn.
In some sectors, regulatory arrangements can strongly influence and even dictate industry structures and processes. When changes occur, and especially major changes such as privatisation, re-regulation and de-regulation, organisations that are well-prepared for events can acquire large market-shares in new or re-defined industry segments, and can take advantage of new revenue-sources or government subsidies. Rukanova et al. (2009) studied international trade, Watson et al. (2010) investigated opportunities in the environmental protection and energy sectors, and Rai et al. (2015) recognised that regulatory measures are determinative of industry structure in the electricity industry.
Key conclusions from the survey of the literature are that the IS discipline has paid only limited attention to regulation, and that the large majority of studies have been compliance-oriented. The author contends that considerable opportunities are available to IS practice and IS research, but that a sufficient framework needs to be established if those opportunities are to be exploited. IS professionals can make practical contributions to the quality of regulatory regimes, as well as to the application of information technologies in support of compliance with those regimes. There are of course also many implications for IS research.
The primary objective of the research reported in this paper is the development and exposition of a framework whereby IS professionals and academics can properly understand regulatory regimes, can identify opportunities for the development and deployment of RegTech, and can conceive, design and deliver appropriate technological support to relevant organisations.
The concept of a framework is of long standing within the IS discipline. See for example Ives et al. (1980), Wand & Weber (2002), Ahuja (2002) and Avgerou (2008). A framework provides structure to the themes and issues in past and future research within a particular domain. Common features of frameworks are descriptions of fundamental concepts and processes, and an arrangement of key elements, often within a two- or three-dimensional matrix of ideas. This paper's purpose differs somewhat from that mainstream, however, in that is concerned not only with IS research but also with IS practice.
Regulatory contexts vary considerably, across such dimensions as ethnic and lingual cultures, systems of law, jurisdictions and industry sectors. On the other hand, there are also commonalities among countries' approaches to regulation, arising in part from 16th-19th century colonialism and in part from 20th-21st century globalisation. Examples include British common law and Napoleonic code law systems, international treaties, multilateral and bilateral trade agreements, international standards (which are particularly significant in the financial services sector), and supranational instruments such as EU Directives and Regulations. To the extent practicable, the framework is intended to be agnostic to the differences, and hence broadly applicable to most circumstances.
This section draws on existing theory as expressed in the literatures of several disciplines, in order to establish a framework within which IS practice and research can recognise and exploit opportunities. The work is not limited to compliance by organisations with regulatory requirements, but extends to regulatory regimes as a whole, adopting the perspectives of each category of organisations active in the field.
The framework comprises four models, presented in the following four sub-sections. The first articulates the nature and purposes of a regulatory regime, and defines the criteria whereby the appropriateness of any particular instantiation can be evaluated. The second presents the layers within which regulatory measures are conceived. The third identifies the various actors within the regulatory space, and the fourth examines the dynamics within that space, as each of those actors seeks to satisfy its own interests. The four sub-models are subsequently used as a basis for identifying and organising many different categories of RegTech. Finally, the potential for application of the framework is demonstrated by means of a topical example.
The concept of regulation is frequently thought of as a matter of law and policy. Its foundations go far deeper, however. General systems theory grew out of observations of biology, where natural processes are subject to other natural processes whose effect is to limit, control or regulate them, giving rise to homeostatis - the tendency of natural systems to maintain the status quo (von Bertalanffy 1940, 1968). During the industrial revolution, a significant breakthrough occurred when Watts invented the steam or 'fly-ball' governor, such that a man-made process was subjected to automated control by another man-made process, rather than by a natural process. Together, these threads gave rise to the insights of cybernetics, whereby sensors provide feedback that enables a controller to monitor a process, effectors enable the controller to influence the process, and successive levels of nested controllers enable complex systems to be managed (Wiener 1948).
The present analysis is not concerned with biological phenomena or manufacturing processes, but with economic and social systems. In these contexts, the motivation for active regulatory measures arises when some class of entities behaves in a manner that has materially negative impacts on other entities. Figure 1 provides a preliminary graphical representation of key entities involved in the regulatory arena, and key relationships among them. The left-hand side of Figure 1 depicts an unregulated state, in which one entity has a negative effect on the interests of a second entity. In the regulated state depicted on the right-hand side, the second entity is a 'beneficiary' of the existence, power and actions of a third entity, usually referred to as a 'regulator', which influence the behaviour of the first entity, the 'regulatee'.
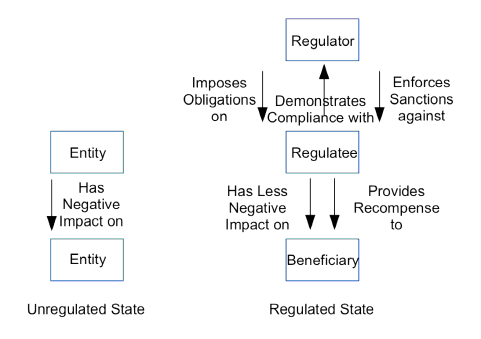
Regulators include tightly-controlled government agencies and relatively independent commissions. Regulatees include corporations, unincorporated business enterprises, government agencies, cooperatives, incorporated and unincorporated associations, and individuals. Beneficiaries include not only all of those categories but also social values such as trust in social and economic institutions, and environmental values.
A simple, useful, but incomplete definition of regulation in economic and social contexts is "instruments used ... to influence or control the way people and businesses behave in order to achieve economic, social or environmental policy objectives" (ANAO 2007). A valuable aspect of that interpretation is its generality, in that formal legal mechanisms are not the only way to influence behaviour. A weakness of the approach, however, is that it is restricted firstly to explicit human actions ("instruments"), and secondly to only those instruments that are applied with the intention to achieve influence ("used to").
Each of the participants in a regulatory regime naturally has its own objectives. For example, an organisation subject to regulatory requirements may adopt a 'responsible citizen' or 'corporate social {and environmental} responsibility' (CSR/CSER) attitude, with an objective of efficiently achieving compliance with regulatory requirements; whereas a 'cowboy' in the same sector may have the objective of avoiding, subverting and ignoring regulatory requirements in order to minimise their negative impacts on the organisation's interests. Similarly, a regulatory agency may adopt the stance of a 'watchdog', interpret its legal authority as widely as possible, and seek to withstand the depradations wrought by lobbying against its activities; or it may stolidly administer the scheme's enabling legislation; or it may perceive itself to have a minimalist, window-dressing role on behalf of government, and may even facilitate industry behaviour irrespective of the harm that it may cause (Drahos & Krygier 2017).
The assumption adopted in this analysis is that the purpose of a regulatory regime is to exercise control over harmful behaviours. That objective is, however, subject to constraints. The most salient of these are that the measures imposed be effective in achieving their aims, and that they be efficient, i.e. that they impose no higher costs on organisations than are justified by the harm being avoided. Many additional factors are involved, however. Criteria for the evaluation of regulatory regimes are discussed in Gunningham et al. (1998). See also Hepburn (2006) and ANAO (2007). An articulated set of attributes of regulatory arrangements that draws on the above sources is presented in Clarke & Bennett Moses (2014) and summarised in Table 1. This facilitates the evaluation of regulatory arrangements, the adaptation of existing schemes, and the development of new schemes.
Adaptation of Clarke & Bennett Moses (2014, Table 2)
_________
This section has articulated the nature and purposes of a regulatory regime, and thereby laid the foundations for examination of the elements and processes that they entail. The following section presents a model of the layers within which regulatory processes are conventionally organised.
Theoretical works on regulation refer to an 'enforcement pyramid', with persuasive measures at the bottom, escalating upwards to aggressive sanctions such as licence revocation (Ayres & Braithwaite 1992). "There is a heavy presumption in favour of starting at the base of the pyramid because dialogue is a low-cost, respectful and time-efficient strategy for obtaining compliance. The responses of the regulatee to interventions drawn from the base of the pyramid are the ones that determine if, how far and when the regulator escalates up the pyramid" (Drahos & Krygier 2017, p.5).
For the present purpose, rather than individual instruments or measures, it is more useful to focus on categories of mechanisms. This paper accordingly proposes the model in Figure 2. This distinguishes layers, based on the degree of formalism and compulsion. Each layer is outlined below, and keyed across from the diagram to the text using numerals (1) through (7).
The foundational regulatory layer is a correlate of the natural control processes that occur in biological systems. It comprises natural influences, by which is meant processes that are intrinsic to the relevant socio-economic system (Clarke 1995, 2014c). Examples of (1) natural regulation include the exercise of countervailing power by those affected by an initiative, activities by competitors, reputational effects, and cost/benefit trade-offs. The postulates that an individual who "intends only his own gain" is led by "an invisible hand" to promote the public interest (Smith 1776), and that economic systems are therefore inherently self-regulating, have subsequently been bolstered by transaction cost economics (Williamson 1979). Limits to inherent self-regulation have also been noted, however, such as 'the tragedy of the commons' notion (Hardin 1968). Similarly, whereas neo-conservative economists commonly recognise 'market failure' as the sole justification for interventions, Stiglitz (2008) adds 'market irrationality' (which justifies the use of circuit-breakers to stop bandwagon effects in stock markets) and 'distributive justice' (in such forms as safety nets and anti-discrimination measures).

An appreciation of pre-existing natural controls is a vital precursor to any analysis of regulation, because the starting-point always has to be 'what is there about the natural order of things that is inadequate, and how will intervention improve the situation?'. For example, the first of 6 principles proposed by the Australian Productivity Commission was "Governments should not act to address 'problems' through regulation unless a case for action has been clearly established. This should include evaluating and explaining why existing measures are not sufficient to deal with the issue" (PC 2006, p.v). That threshold test is important, in order to ensure a sufficient understanding of the natural controls that exist in the particular context. In addition, regulatory measures can be designed to reinforce natural controls. For example, approaches that are applicable in a wide variety of contexts include adjusting the cost/benefit/risk balance perceived by the players, by subsidising costs, levying revenues and/or assigning risk.
All of the other layers in Figure 2 represent interventions into natural processes, and comprise 'instruments' and 'measures', generally designed with an intention to achieve some end. That end is desirably to curb harmful behaviours and excesses, but in some cases the purpose is to give the appearance of doing so, in order to hold off stronger or more effective interventions. Such 'counter-regulatory' phenomena are discussed in a later section.
From the viewpoint of IS practitioners and academics, the exposition of the framework to this point has provided background, but the role of IS has not yet emerged. Information, and the design of systems to handle information are, however, inherent in all of the remaining six layers of the heirarchy.
The second-lowest layer, referred to in this paper as (2) infrastructural regulation, is a correlate of artefacts like the mechanical steam governor. It comprises particular features of the infrastructure that reinforce positive aspects and inhibit negative aspects of the relevant socio-economic system. Those features may be byproducts of the artefact's design, or they may be retro-fitted onto it, or architected into it. (The first steam-engines did not embody adequate controls over excessive steam-pressure. The first steam-governor was a retro-fitted feature. In subsequent iterations, however, controls became intrinsic to the design of steam-engines). Information technology provides many opportunities, and even mechanical controls are feasible, through the application of robotics. For example, dam sluice-gate settings can be automatically adjusted in response to measures of catchment-area precipitation events or changes in feeder-stream water-flows. One popular expression for infrastructural regulation in the context of IT is 'West Coast Code' (Lessig 1999, Hosein et al. 2003).
At the uppermost layer of the regulatory hierarchy, (7) formal regulation exercises the power of a parliament through statutes and delegated legislation such as Regulations. In common law countries at least, statutes are supplemented by case law that clarifies the application of the legislation. Formal regulation demands compliance with requirements that are expressed in more or less specific terms, and is complemented by sanctions and enforcement powers. Lessig underlined the distinction between infrastructural and legal measures by referring to formal regulation as 'East Coast code'.
Regulation of the formal kind imposes considerable constraints and costs. Several intermediate forms exist, which reduce those imposts, at the cost of also reducing the effectiveness of the regulation. The lowest layer of these intermediate forms is (5) organisational self-regulation. Examples include internal codes of conduct and 'customer charters', and self-restraint associated with expressions such as 'business ethics' and 'corporate social responsibility' (Parker 2002).
The mid-point of the heirarchy is (4) industry sector self-regulation. In many sectors, schemes exist that express technical or process standards. There are also many codes of conduct, or of practice, or of ethics, and some industries feature agreements or Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) that are claimed to have, and may even have, some regulatory effect. However, by their nature, and under the influence of trade practices / anti-monopoly / anti-cartel laws, these are in a substantial proportion of cases non-binding. Further, to the extent that they have any direct impact, it is only on those organisations that choose to adopt them, which seldom includes the 'cowboys' in the industry, which tend to be responsible for a disproportionate amount of the harm that the industry causes (Sethi & Emelianova 2006). Another mechanism used in some fields is accreditation ('tick-of-approval') schemes, such as so-called 'privacy seals'. These are best understood by describing them as meta-brands. The conditions for receiving the tick, and retaining it, are seldom materially protective of the interests of the nominal beneficiaries (Clarke 2001a, Moores & Dhillon 2003).
The effectiveness of the two self-regulatory layers, perceived from the viewpoint of the entities that are meant to be beneficiaries of regulatory arrangements, generally falls well short of the promise. Activities conducted under the 'self-governance' label may provide some limited safeguards and the prospect of mitigation of harmful impacts, but they are primarily motivated by the avoidance of harm to the regulatees rather than the assurance of protections for beneficiaries. Braithwaite (2017) notes that "self-regulation has a formidable history of industry abuse of privilege" (p.124). The conclusion of Gunningham & Sinclair (2017) is that 'voluntarism' is generally an effective regulatory element only when it exists in combination with 'command-and-control' components.
Other, intermediate forms have emerged that have been claimed to offer greater prospects of achieving the regulatory objective of protecting against inappropriate behaviour and excesses. In a number of areas, convincing arguments can reasonably be made by regulatees to the effect that government is poorly placed to cope with the detailed workings of complex industry sectors and/or the rate of change in industries' technologies, practices and structures. Hence, the argument proceeds, parliaments should legislate no more than a framework, and enable details of the scheme to be developed within that framework.
During the last four decades, several forms have emerged that are intermediate between (often heavy-handed) formal regulation and (mostly ineffective and excusatory) self-regulation. In Grabowsky (2017), the notion of 'enforced self-regulation' is traced to Braithwaite (1982), and the use of the term '(6a) meta-regulation', in its sense of 'government-regulated industry self-regulation', to Gupta & Lad (1983). See also Parker (2007). In parallel, the notion of '(6b) co-regulation' emerged (Ayres & Braithwaite 1992, Clarke 1999). Broadly, these approaches involve enactment of a legislative framework, but expression of the details is established and maintained by means of a negotiation process among the relevant parties. The participants necessarily include at least the regulatory agency, the regulatees and the intended beneficiaries of the regulation, and the process must reflect the needs of all parties, rather than institutional and market power. In addition, meaningful sanctions, and enforcement of them, are intrinsic elements of a scheme of this nature.
However, the promise of enforced self-regulation, meta-regulation and co-regulation has seldom been delivered. Commonly, the nominal beneficiaries are effectively excluded from the negotiations, and terms are not meaningfully enforced, and may even be unenforceable (Balleisen & Eisner 2009). Schemes of this kind that lack such fundamentals - typically in the form of 'guidelines' and 'MoUs' but sometimes masquerading under the title of 'Codes' - are referred to in this analysis as (5) pseudo meta- and co-regulation.
A real-world regulatory regime seldom contains elements from all of the layers discussed in this section. The purpose of Figure 2 is to identify all of the possibilities, from which the designer of a regulatory scheme needs to select one, or devise some combination, that is appropriate to the particular context, and that satisfies the criteria identified in Table 1. In practice, however, many regulatory regimes commonly comprise elements of more than one of the layers in Figure 2: "in the majority of circumstances, the use of multiple rather than single policy instruments, and a broader range of regulatory actors, will produce better regulation [by means of] the implementation of complementary combinations of instruments and participants ..." (Gunningham & Sinclair 2017, p.133).
This model has considerable relevance for IS practitioners and academics, because of the central role played by information and its management, and by the incorporation into systems designs of features that variously support, incentivate and enable regulatory effects. The following two sections identify the entities involved in regulatory regimes, and their behaviours and interactions. Together the four models provide the necessary basis for identifying and addressing opportunities for IS practice and research.
A preliminary model was presented in Figure 1 above, identifying three categories of entity involved in regulatory schemes, referred to in this paper as regulators, regulatees and beneficiaries. This section expands that preliminary model in order to identify the much fuller set of players that may take to the field across all of the regulatory layers identified in Figure 2.
In Figure 3, the three central players remain unchanged. They have been joined, however, by many other entities. Considering firstly the upper areas of Figure 3, any one regulatee may be subject to multiple regulators (e.g. relating to the corporations law, tax, occupational health and safety, and product-specific aspects such as food, chemicals or financial advice). Each regulator is created, empowered and resourced by a parliament, and that parliament can vary its terms of reference, and can further empower, neutralise or disestablish it. In some cases, a regulator may be accountable directly to the relevant parliament, but the more common model is for the regulator to report to a designated Minister through a high-level agency.
Regulators need to research, consult, draw on the services of consultants, negotiate, draft and promulgate. Later they need to investigate, and may enforce, sue and prosecute. Inevitably, their reports to the portfolio agency or the parliament involve a degree of defence against attacks from aggrieved regulatees and their associations, and, in most cases less powerfully, from aggrieved beneficiaries. Other policy agencies may also influence the regulator's behaviour. In some sectors, a further role is evident, sitting astride the regulator / regulatee boundary. For example, stock exchanges play an intermediary role in relation to listed corporations, registrars, brokers and traders; and bank industry clearing associations perform similar functions in relation to participants in payments systems.

Turning attention to the middle block of Figure 3, regulatees' compliance with relevant regulatory schemes is, at least in principle, subject to audit, although the extent to which this is implemented and effective is variable, and in some schemes the auditor is so closely associated with the regulatee as to be indistinguishable from any other consultant. Formal Industry Standards have a degree of influence on industry activities, usually very substantial in the case of technical standards, whereas process standards sometimes have rather less impact. Some regulatees contribute to the formation of such Standards. Regulatees club together in industry associations, and may seek to use an industry tick-of-approval. Key players are supported by consultants. Ombudsman schemes handle complaints from beneficiaries, and may have some influence over aspects of regulatee behaviour. In some circumstances, beneficiaries may themselves have the capacity to sue and to achieve recompense through courts, tribunals or other schemes.
Given the scale of organisations and their activities, all players all heavily dependent on IT, and on information systems that manage the relevant data, support decision processes, and in some cases automate decision-making and reporting. The following section, which considers opportunities in the regulatory space, provides many specific examples.
RegTech providers service the needs of players in the regulatory space, and hence they generally accept regulatory schemes as they are, and contrive ways in which players' needs can be served. However, very substantial resources are expended in achieving regulatory objectives, and RegTech providers develop a deep understanding of the mechanisms involved. The scope therefore exists for them to convey to regulators the scope for adaptations to regulatory schemes in order to better achieve the scheme's objectives and/or to avoid undue process inefficiencies, i.e. to better satisfy the criteria presented in Table 1 above.
The structure of regulatory schemes, as modelled in Figures 1-3, might be regarded as somewhat adjacent to IS. On the other hand, support for the business processes involved, including data capture, maintenance and analysis, and workflows within and between organisations, represent heartland for IS practice and research, and the effectiveness, efficiency and adaptability of IS conception and design is heavily dependent on a sufficiently deep appreciation of the industry context.
The dynamics of a regulatory scheme are driven by the motivations and behaviours of the players. This section outlines the primary factors arising in relation to the three main categories - regulatees, regulators and beneficiaries.
Regulatees that are subject to formal regulation adopt various stances (Greenaway et al. 2015). The 'responsible citizen' approach involves a positive attitude to compliance, whereas some organisations treat it as low-priority administrative overhead, and the 'cowboy' segment of the industry flouts the rules. Consultancies develop and sell ways in which their clients can inexpensively comply with formal regulation, including software products featuring data management capabilities, but also how they can mitigate, circumvent and even nullify its impacts.
As noted earlier, formal regulation imposes considerable constraints and costs (Fisher & Harindranath 2004). As a result, regulatees invest a great deal of time, effort and money in order to avoid, minimise and dilute formal regulation. Political influence may be used to capture the regulator, relevant government agencies, one or more Ministers, a political party and/or the parliament (Shapiro 2012). Tools commonly used at the level of industry associations and by very large corporations include lobbying of Ministers in parallel with negotiations with regulators and other government agencies, codes of conduct, meta-brands, and industry-funded complaints schemes. An examination of the dynamics underlying the failure of industry self-regulation in a particular sector is in King & Lennox (2000).
Meanwhile, individual organisations are frequently able to buy off the regulator's attention by giving 'enforceable undertakings' to stop breaching the law, or entering into 'consent orders', perhaps coupled with the belated inclusion of reviews of compliance within their audit programs. The public wonders why breaches of the law by the politically weak are prosecuted, whereas miscreants that are large or powerful are forgiven. The credibility of such instruments is destroyed when regulators fail to enforce 'enforceable undertakings' that have clearly been breached, as has been the case with, for example, the US Federal Trade Commission (EPIC 2011).
Reference was made earlier to regulators playing roles depicted as activist watchdog, passive administrator or industry-friendly facilitator. Because regulators are generally constituted by statute, the scope for them to determine which of those roles they play depends to a considerable extent on the intention of the parliament. This may be determined by the Minister or the agency that drives the legislation through. A regulatory initiative may be fully committed to control over negative impacts on beneficiaries. More commonly, however, under pressure of lobbying from associations representing large volumes of commercial activity, profit and jobs, the regulatory design to at least some degree compromises the definition of, or the achievement of, the nominal regulatory objectives.
In many cases, a portfolio agency is provided with sufficient delegation from the parliament, e.g. in relation to the resourcing of the regulator, appointments to key positions within it, and the approval of codes, with the result that it can vary the parameters set by the parliament, possibly tightening them, but more likely, under lobbying pressure, easing the constraints on regulatees. Consultancies, in strategic, legal, compliance, marketing, public relations and government relations areas, provide services to regulatees and their associations in relation to the most effective pressure-points among Ministers and agencies, and the techniques for achieving compromise of regulatory designs or processes. The practicalities of gaming regulatory systems are matched by literatures on the political economy of regulation (e.g. Libecap 2008), and on game-theoretic analyses of interactions between a regulator and the (frequently more powerful) regulatees (e.g. Madani 2010).
Beneficiaries are in most cases less well-resourced and less well-informed than the other players. Adjustments for power and information asymmetries are possible, such as class actions, legal aid, representative complaints, test cases and an adequately resourced champion, of the nature of a 'public defender's office'. In many contexts, however, these measures are absent or defective. Ombudsman arrangements may exist, although it is common for the bases of complaint to be limited, and uncommon for such complaints organisations to have significant powers to force change and achieve restitution, let alone power to impose effective sanctions for serious or repeated breaches. An alternative interpretation of such schemes is as an 'expectations management' mechanism, to reduce complainants' expectations of what the process can achieve (Gilad 2008).
These realities of 'regulatory play' need to be understood by IS executives, practitioners and academics, in order that IS can play an effective role in both compliance endeavours by regulatees, and the functional activities of regulators.
In the pre-theoretic phase in a new sub-field of IS, a research framework provides structure to themes and issues, including descriptions of fundamental concepts and processes. The models presented in the preceding four sub-sections represent such a framework for the new sub-field of RegTech.
The combined understanding of regulatory space, layers, players and plays enable IS executives, practitioners and academics to perform the 'sense-making' activities that necessarily precede the conception, design, development and deployment of new IS, and the adaptation of existing IS. The first model provides a gross model of the space, including the function that regulation performs, the central players, the relationships among them, the processes whereby regulation is achieved, and the criteria whereby the appropriateness or otherwise of a regulatory regime can be evaluated. The second section presents a more detailed model of the processes, the third provides a detailed articulation of the players, and the fourth delves more deeply into the interactions among the players.
The following sections draw on and apply the concepts and insights provided by the framework, in order to identify contributions that can be made by technology, and by the IS profession and discipline.
In the first UK government report on RegTech in the financial sector, a scatter of technologies were mentioned: "real-time transaction analysis, online registration, standard data formats, standard (risk-weighted) asset indices, automated reporting, open-source compliance systems, and big data analytics" (UKGOS 2015, p.47). All of these are clearly within-scope of the IS profession and discipline. However, this article proposes a considerably broader vision. It encompasses those aspects; but the models in the previous sections enable the identification of far more instances of RegTech, and underline their relevance to all entities that are participants in regulatory schemes, and across all industry sectors.
Firstly, a first cluster of opportunities for IS practice and theory can be identified in the second model, the regulatory layers depicted in Figure 2, within layer (2) infrastructural regulation. There are many ways in which information infrastructure can be harnessed to regulatory tasks. An important example, expressed in its most generic form, is the detection of exception conditions. For example, if a regulator has access to a real-time flow of transaction data, it can implement algorithms or rule-sets in code in order to achieve the detection of unusual occurrences very shortly after they happen. Retrospective analysis of transactions over time can discover unusual patterns. An important application of the principle that can be easily overlooked is the detection of the absence, or of markedly low volumes, of exception reports. In an effective scheme, pre-planned actions may be triggered, and the details are notified to appropriate staff for detailed investigation.
There are many applications of these ideas. For example, a stock exchange - which is both a regulatee supervised by a government agency and a regulator of behaviour in the market that it operates - can implement continuous, automated transaction monitoring as a means of compliance assurance (Arner et al. 2016, Winn 2017), and can automatically suspend trading in one stock, or in all of them, when signs of spiralling bandwagon effects are detected. Similarly, a consumer appliance can auto-report malfunctions and low battery-power to its owner. It might also auto-report some categories of malfunction or apparent abuse to the appliance-supplier. All such activities are within-scope of the IS profession and discipline.
In addition to the monitoring of stock market transactions for patterns indicative of illegal behaviour, financial transactions tracking and analysis has long been undertaken by specialist government organisations such as Fincen in the USA, Fintrac in Canada and Austrac in Australia. Health care claims are examined for evidence of fraudulent invoicing, over-servicing, and 'doctor-shopping' in order to acquire supplies of controlled drugs. Many further possibilities exist in such areas (Ngai et al. 2011). Registration and licensing approaches require the support of backend registry systems and a public front-end. Regulators' enforcement arms need information systems to support own-motion investigations, complaints-handling, and litigation case management.
Regulatees too can apply similar approaches, for example by pre-defining online patterns associated with misbehaviour, and designing the infrastructure so that instances are detected and relevant staff are alerted or countermeasures are automatically deployed. The example considered in the following section identifies a range of specific forms of embedded regulatory measures. To the extent that predictions about the 'Internet of Things' come to fruition, many more such opportunities may emerge. These may have to be imposed by regulators, but it is also possible that they may be innovations by regulatees. Once again, all of this is IS-relevant activity.
Switching from the second-lowest to the highest layer of the model of the regulatory hierarchy - (7) formal regulation - statutory regulatory schemes bring with them specific requirements, often involving data management involving considerable volumes of transactions. This can also arise with co-regulatory and self-regulatory schemes. These responsibilities involve detection, measurement, recording, analysis, response and reporting. Such obligations and undertakings are capable of being directly supported by IS, and in many cases the functions can be performed using contemporary technology considerably more effectively than legacy systems have achieved.
One benefit that can be sought is effectiveness. For the regulator, this may mean control over undesirable behaviours and negative impacts. For the regulatee, on the other hand, the focus may be on compliance with legal requirements or formal undertakings, through the detection of organisational behaviour that conflicts with corporate policies or defined business processes. Other benefits can include reductions in financial costs and in less frequent deflection of executive attention away from the organisation's primary business. Further, where a system provides a regulatee with early warning, it becomes feasible to have the problem understood and under control within the timeframe in which it needs to be reported to the regulator. This obviates not only problem escalation, but also resource-wasting interactions with the regulator and unnecessary negative publicity. The chances of avoiding both sanctions and reputational harm are greatly improved. This may not appear to be as exciting as IT alignment, strategic information systems, business process re-engineering and technologically-driven disruption, but the incorporation of such features in IS can make considerable contributions to the fulfilment of the organisation's mission.
Among regulatees, in many contexts, compliance practices have been poorly resourced and inadequately supported, and hence organisations need to catch up with where they should already be. As a result, many opportunities for RegTech providers are quite straightforward to address. One important and quite generic area, for example, is data protection. That term is commonly used in relation to personal data, but it is just as applicable to data with intrinsic value (such as financial transactions, registry data that evidences ownership, and the burgeoning instances of 'wallets' containing digital cash such as Bitcoins), data with security connotations (particularly decryption keys, and authenticators such as password and private signing-keys), data with operational value (such as that used to control, or support control of, physical operations such as flows of water and gas, and movements of trains and boats and planes), and data demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements (Clarke 2013).
Regulatory schemes commonly require safeguards against data access by inappropriate organisations and individuals. Some of these measures are preventive, such as vulnerability scanning. Others support detection and investigation, including intrusion detection and audit-log analysis. Access by 'insiders' is frequently a bigger threat than hacking and social engineering; so there is also a need for safeguards against inappropriate access to and use of data by individuals and organisations that have the means to do so, i.e. that are authorised to access and use data for some purposes only, but that act outside their authorisations. The techniques of access control, audit trailing and automated monitoring of audit trails were well-known a quarter-century ago (Clarke 1992). Yet the implementation of such basic tools remains almost as poor as at that time, as evidenced by the continual flow of data breach reports (Lord 2017).
A further important aspect of security is data integrity safeguards, through the prevention of unauthorised changes, corruption and loss of data, e.g. through periodic integrity-checking, and backup and recovery processes (Clarke 2016c). In many organisations, the implementation even of 'baseline security', i.e. relatively unsophisticated measures, would greatly improve performance against regulatory requirements (Clarke 2015). Data protection, access control and integrity matters are mainstream IS territory, and primary areas in which the proposed broad interpretation of RegTech offers opportunities to IS executives, practitioners and academics.
Another set of techniques of broad relevance across both formal regulation and the various kinds of self-regulation is incident management (e.g. ENISA 2010). This not only caters for reports of specific threats to the security of data, but also underpins the management of many other kinds of risks. A very similar kind of system can provide support for complaints management (e.g. ISO 2006). Depending on the context, this may be internal to the organisation's customer relationship management system, or it may also be integrated with an industry ombudsman's system and/or integrated with a regulatory agency's supervisory or audit system.
Another application that can offer value is a product register maintained by a product manufacturer or importer, with life-cycle capture of data about each instance of the product (e.g. Hobbs 2004). This can enable, for example, tracing of faulty or contaminated products, and product recalls (Jansen-Vullers et al. 2003). IS features that are well-established in some contexts already (such as aircraft spare-parts, controlled tradable items such as explosives, drugs and weapons, and the more valuable kinds of livestock) can be exploited in other contexts as well. Considerable benefits can be gained from the integration of such features into the customer relationship management function, including warranty databases. Suppliers can achieve enhanced customer loyalty and the default-purchasing, price-insensitivity and follow-on low-cost revenue that customer loyalty gives rise to. Similarly, trusted intermediaries (such as consumer associations) can utilise forms of RegTech to establish and maintain linkages between members, on the one hand, and, on the other, service-providers, such as insurers, and regulators. This is an example of how IS practitioners and researchers can leverage opportunities arising from RegTech by integrating them with marketing and other strategic initiatives.
Another relevant category of RegTech is automated statistical reporting. Some outputs need to be designed to assist the entity's own management to understand the operations that are subject to regulatory measures and to detect, investigate and address problems as they arise. Other outputs can support compliance responsibilities, by promptly accounting to the relevant regulatory agency. Such systems can improve effectiveness and reduce costs associated with, for example, anti-discrimination and positive discrimination measures (relating to gender, disability, age, ethnic background, sexual orientation, etc.). Although the specific requirements vary, occupational / workplace health and safety (OH&S / WHS) gives rise to obligations in relation to the design and inspection of places and processes, to staff training, to sufficiently frequent reminders of good practice, and to reporting of actions taken and outcomes achieved. Systems to support these responsibilities, combined with features of human resources systems, can ensure that educational requirements are satisfied, and occupational registration and licensing provisions are complied with. Another example of a generic regulatory responsibility that can be supported by RegTech is compliance with energy efficiency standards (Watson et al. 2010). The exploitation of every such opportunity involves IS.
This section has identified a wide range of opportunities inherent in the four models of the regulatory space, layers, players and plays that make up the research framework. Although the primary emphasis in this section has been on the large-scale activities of corporations, and support for the processes managed by regulator, needs also exist among the intended beneficiaries of regulation. Consumers, citizens and small business alike need guidance on how to go about dealing with organisations that are failing to fulfil their obligations or are otherwise behaving unreasonably. The current post-customer-service mode of business and government operations places heavy reliance on customers helping themselves and one another, and hence it is increasingly common for problems to fester rather than being solved. This has increased the need for electronic tools that provide active guidance as to what requirements regulatees are subject to, which regulatory agencies exercise what powers over which regulatees, and how to initiate formal complaints processes. Many regulatory agencies provide very limited assistance in these areas, and hence scope exists for RegTech to deliver such services, provided that viable business models can be contrived.
A structured summary of regulatory measures mentioned during the analysis is provided in Annex 1. Those measures are generic, in the sense of being applicable in a wide range of contexts. Considerable opportunities also exist for RegTech in specific industry sectors, because the requirements in different areas are so diverse. Annex 2 provides a gross analysis of opportunities, utilising the Standard Industrial Classification and PC (2006, pp.viii-xiv) in order to identify relevant industry sectors and indicate factors that need to be reflected in the design of RegTech to suit each sector's needs. In Annex 3, major categories of RegTech measures are organised by regulatory layer and regulatory player.
This section has demonstrated that the framework presented in s.3 enables the identification of a rich suite of opportunities in the RegTech arena for IS practice and IS research. Although instances of most of these applications pre-exist the emergence of the RegTech notion, its articulation by means of the models presented earlier provides a comprehensive but cohesive view of the field, and a vision of regulatory activities that are integrated across all relevant organisations within each particular context. The following section applies the framework to a particular context.
The previous section has drawn directly from the four models that make up the framework, in order to identify opportunities for IS practitioners and researchers to apply the RegTech notion. This section complements that broad-scale approach by undertaking a 'deep-dive' into one particular context in which regulatory challenges exist, and hence opportunities need to be sought out.
Suitable case studies were accordingly sought in the literature. Such case studies as were located are, however, strongly oriented towards the political economy of regulation (e.g. Lynch & Vogel 2001), regulatory law (e.g. Minor 2014), or management (e.g. Lynes & Andrachuk 2008), and lack the detail needed for the purpose at hand. What is needed is a systemic view of the way in which a regulatory regime was designed to work and/or actually works, including sufficient information about the current IT applications that support the players. An example of such an approach is in Duncombe & Heeks (2003), in the specific context of ethical trade. This commences with a model of the players, and then extends to models of processes and data flows.
Consideration was given to conducting a suitable case study as part of the current phase. That is, however, a substantial project in its own right, and adequate presentation of it requires an article of much the same size as the present one. An example was therefore sought of the size of a vignette rather than a full case.
The author has previously published on the regulation of the public safety impacts of drones. Drones might seem an inappropriate example to consider in an IS journal. On the other hand, drones involve a set of interacting artefacts and human activities that handle a considerable amount of data; they are an active area of ongoing development; they are already having significant economic and social impacts; and they warrant closer attention by IS practitioners and academics than they have been given to date. Moreover, drones provide an opportunity to apply the framework presented in this paper to various forms of regulatory regime, including not only those that already exist, but also alternative approaches that have been proposed.
There are weaknesses in this choice as an appropriate basis for evaluating the framework presented in this paper. For example, it includes some speculative elements, and it lacks independence from the person who devised the framework. Nonetheless, drone regulation provides a basis for gaining valuable insights into the framework's usefulness. Background analysis is in Clarke (2014a, 2014b). A range of actual regulatory regimes is presented and discussed in Clarke & Bennett Moses (2014). Some specific proposals are outlined in Clarke (2016b). The remainder of this section defines the categories of drones that are being considered, applies the framework, with particular reference to the model of players, and cross-checks the theoretical account against contemporary regulatory regimes in three countries.
There are many kinds and sizes of both drones. There are also many kinds of drone applications, and the military, quasi-military, commercial and recreational contexts give rise to many different risks that need to be managed and conflicts of interest that need to be balanced. However, small drones for commercial and recreational use provide a sufficiently rich field of current realities and future possibilities. The scope of the discussion is accordingly limited to that category.
Some degree of (1) natural regulation can be detected in relation to dangerous drone design, manufacture and use exists, but its effectiveness is somewhat muted. The risk of harm to the pilot is largely limited to take-off and landing manoeuvres, and at that point the device's altitude and velocity are low and the pilot's concentration is at a natural peak. During flight, on the other hand, the altitude, velocity and hence capacity for harm are higher, the pilot's concentration is variable, and the threats that the drone embodies afflict other people rather than the pilot. Because recreational devices are inexpensive, the pilot, even if they are also the owner, may well be in an experimental frame of mind, and hence careless, perhaps cavalier, and even reckless, with respect to risk to the drone. That attitude may give rise to considerable risk to other people's property, and to their personal safety.
The pilot is separated by some physical distance from the drone's area of operation, and from people affected by it, giving rise to a degree of social distance and hence of dissonance between the parties' valuations of the levels of nuisance and threat. This rises considerably where the device is not in Visual Line of Sight (VLOS), and where control depends on First Person View (FPV - using vision transmitted from an onboard camera to a screen or goggles), or is entirely instrument-based. Unless conditions exist in which physical retribution is feasible (e.g. through proximity and/or recognisability), or financial retribution may arise (e.g. through a lawsuit), there may be limited contextual cues to convey other-party displeasure or risk to the pilot. Similarly, the risk of reputational harm is only in particular circumstances likely to act as a constraint on pilot behaviour.
One of the tenable depictions of a drone is as 'a flying computer'. Adopting this perspective creates considerable possibilities in relation to (2) infrastructural regulation, all of which fall squarely within-scope of IS research. A wide range of functions have been considered, in some cases at least trialled, and even proposed as mandatory capabilities for small drones. Range limitations, sometimes referred to as 'geo-fencing', can prevent drones from straying into 'no-go zones' or too far from the point-of-origin or the pilot's current location. Movement outside the pilot's line of sight can be precluded, by reference to measures of distance and signal attenuation. Monitoring of a light-sensor can prevent night-flying. Multiple communications channels can be used in order to reduce the extent to which telemetry and control signals are interrupted. Some form of fail-soft approach to loss of contact can be mandated (although 'remain-in-place' has limited value in the case of craft with a short flight-time, and some implementations of the 'auto-return-to-origin' stategy is fraught with challenges). Collision-sensing and collision-avoidance are highly desirable, but at present the capabilities are not well-developed. Every such application of IT, although it requires technical aviation and/or geo-spatial expertise, falls within-scope of the IS profession and discipline.
Beyond infrastructural regulation, many possible measures can be conceived that would address public safety risks arising from drones. Those that are most appropriately implemented as formal regulation are discussed first. The subsequent paragraphs identify further measures that are tenable not only as (7) formal regulatory measures but also as (6) co-regulation, (4) industry sector self-regulation and (3) organisational self-regulation. Care is needed to assign responsibilities to appropriate regulatees. The generic model in Figure 3 above, which forms part of the framework, is customised in Figure 4 below, in order to provide a model of the players within the drone industry sufficient to support the analysis.
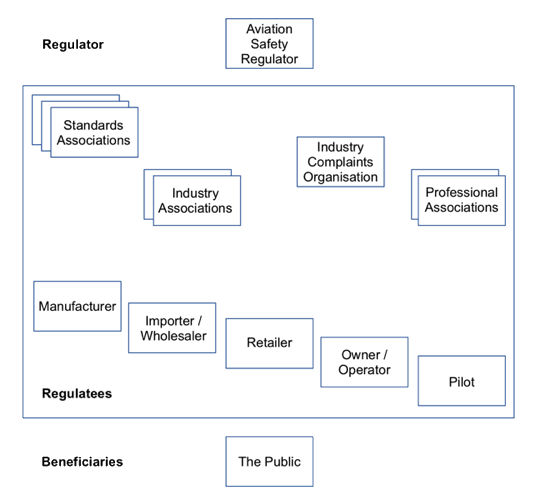
In the area of (7) formal regulation, reviews can be conducted of existing criminal offence provisions, and adaptations made where necessary, in relation to such matters as violent acts against persons and property, criminal negligence, and interference with computer operations and communications. This is needed in order to assess the extent to which existing measures are adequate, and to ensure that technological change has not undermined protections that the public reasonably expects to be in place.
Express responsibilities can be imposed on manufacturers and importers in relation to such matters as:
These may be accompanied by compulsory supplier warranties, and even strict liability. This may sound draconian. On the other hand, gravity, drone velocity and unshielded rotor-velocity combine to generate a material threat-level in even a modest-sized drone, and provisions of such kinds already apply to larger aircraft and to individual use of motor vehicles of all sizes.
Of direct relevance to IS practice and research, a registration scheme can be imposed on drones, i.e. a requirement on manufacturers and importers to identify each aircraft and provide details into a registry. This may, alternatively, be a licensing scheme, whereby the technical specifications of each model must be provided, and possibly be subject to certification, and even testing. This could be implemented by, for example, extension to motor vehicle or aircraft registration or licensing schemes.
Another possibility is to impose a registration scheme not on the drones, but on the entities that acquire and/or that undertake operation of a drone and/or who pilot a drone. This may, alternatively, be a licensing scheme, whereby individuals are subject to training requirements and pre-testing prior to being authorised to operate or pilot any drone and/or a particular model of drone. This could be implemented by extension to driver or pilot registration or licensing schemes - which is within-scope of even the most restrictive conception of IS practice and research.
Any entity that provides a drone to a person who intends to operate it can be required to communicate specified information to them, which could include an outline of relevant laws and sanctions, operating instructions, and contact-points for insurers and model aircraft associations. Systems can be readily designed to assist the administration of such schemes, and to demonstrate compliance with the requirements.
Third party insurance could be mandated for drone operators. A requirement, or alternatively a strong incentive, could be provided to operators to join an approved model aircraft association, in particular by persuading such associations to negotiate third party insurance coverage for members.
A number of further measures are arguably unsuitable for embedment in statutes, because they necessarily involve considerable levels of technical detail. The (6) co-regulation approach, on the other hand, enables considerable input from regulatees and beneficiaries, and promulgation of a Code that reflects the realities of the activities being regulated. Aspects of drone design that could be addressed in this way include the set of technical features that a drone must embody (possibly rapidly changing during the next two decades), and the quality assurance processes that must be applied during manufacture. Other possibilities are the levels of automation that are and are not permitted, the nature of the override capabilities that are to be available to the pilot, and the categories of decision-making and actions that are precluded from being delegated to devices. Similarly, the broad notion of transparency in order to enable informed decision-making and accountability is better operationalised in a Code backed by a statute rather than within the legislation itself.
An alternative approach of the nature of (4) industry sector self-regulation can ensure that specific safeguards are built into drones by specifying formal Industry Standards. This would facilitate the application of insights from relevant pre-existing Standards such as those for aircraft, vehicles, dangerous equipment and toys. In addition to technical matters, Standards can also specify requirements of and details concerning processes such as manufacturing and product quality assurance. However, Standards bodies are generally dominated by representatives of regulatees, and specific measures may be needed to achieve participation by representatives of the beneficiaries of the regulation.
Industry associations can play further roles in the regulation of drones. The primary motivation for them to do so, however, is as a means of holding off more interventionist measures. As a result, such approaches will seldom deliver satisfactory outcomes from the perspective of the beneficiaries. Possible activities include the provision of information to purchasers, training, and encouragement to join model aircraft associations. In addition, an industry association can operate or fund a complaints-handling organisation. Some of these measures require the support of purpose-designed IS.
There may also be a role for (3) organisational self-regulation. Organisations can voluntarily implement design features and quality assurance processes, provide information to customers, and promote membership of model aircraft associations. Such activities would most likely be undertaken by suppliers whose marketing strategy is based on product differentiation, whereas those whose focus is on low-cost offerings would rationally avoid voluntarily adding to their overheads.
The analysis in this section has been empirically-based, but largely theoretical in nature. Hence a check against some actual regulatory schemes is desirable. The US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has rules for business uses of small drones (referred to as UAS), up to to 55lbs / 25kg (14 CFR part 107). Airworthiness certification is not required, but a 'remote pilot airman certificate' must be held by the pilot or by a person directly supervising them. Except in emergencies or where a waiver is granted, VLOS operation is mandatory, separation from people and controlled airspace is required, indoor operation and night operation are not permitted, and maximum speed of 100 mph (87 knots) and a maximum altitude (generally) of 400 ft are both mandated.
For 'fly for fun' / recreational use of drones up to 25kg in the USA, a delegated arrangement is in place (Special Rule for Model Aircraft, at P.L. 112-95, Section 336). This requires operation "in accordance with a community-based set of safety guidelines and within the programming of a nationwide community-based organization". FAA sought to impose a pilot registration scheme on recreational drone users in December 2015 (FAA 2016), but it was struck down in the courts in May 2017 (Taylor v. Huerta, USCA No. 15-1495, 2015). It is unclear whether the existence or otherwise of a registration scheme would have made much difference to public safety. The recreational-use provisions in particular are at the 'light-touch' end of the spectrum outlined in the earlier part of this section.
Within the European Union, responsibility for the regulation of small drones is primarily at national level, and there is accordingly considerable diversity and lack of clarity about the requirements, even for professional use but particularly for recreational use. During 2017, the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) published a set of posters providing guidance in relation to five categories of drone, identified as C0 (<250gm), C1 (to 900gm), C2 (to 4kg), C3 and C4 (to 25kg). Whether and when drones will begin carrying the relevant marking is unclear. The regulatory measures are a gradated sub-set of factors, at a fairly fine level of granularity (EASA 2017, p.72). All of these regulatory regimes are encompassed by the framework presented in this paper, and most of the specific requirements are addressed within the theoretical discussion in the earlier part of this section.
The Australian regulator is the Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA). The relevant statute is expressed in general terms, and CASA issues Regulations, a form of delegated legislation. CASA formalised regulatory arrangements for drones in 1998-2002, and amended them in 2016. For large drones used for commercial purposes, the provisions are based on those for aircraft with on-board pilots, and include compulsory registration of aircraft and operators; training, testing and licensing of pilots; sanctions; and an enforcement regime.
However, provisions relating to commercial use of drones up to 25kg in weight were significantly relaxed in September 2016, such that they are now based on registration rather than certification, and it is only necessary to "notify CASA at least five business days before their first commercial flight and agree to operate by the standard operating conditions and the guidance in advisory circular (AC) 101-10" (CASA 2016). Meanwhile, Alphabet's Project Wing has been granted unpublished but apparently substantial exemptions from the normal requirements, in order to conduct trial deliveries of pizzas and pharmaceuticals in suburbs of the national capital. The pattern is consistent with that of a regulator that has been captured by the regulatees. In the area of aviation safety, public opinion is subject to very large mood swings following major accidents, and knee-jerk changes to those Regulations appear likely sooner rather than later.
Non-commercial uses of drones, variously referred to in CASA documents as "for sport or recreation" and "for fun", are subject to longstanding and even more light-touch regulatory arrangements. Remarkably, these apply not only to small drones under 2kg, but all the way up to 150kg devices (CASA 2002). The guidance provided (CASA 2017) fails to even mention that CASA has regulatory responsibilities, can levy fines, and occasionally does so. In the past, fines have mostly been imposed only when the regulator's hand has been forced by public opinion - for example, where drones have crashed on and near Sydney Harbour Bridge, which means that the pilot was not only flying in breach of distance-separation rules but also within an area subject to air traffic control. During 2017 and 2018, it appears that, nationwide, only a very few fines were issued. A constructive measure has been the release of an app that enables drone users to check their proximity to air-traffic-controlled areas. However, this does little to affect the behaviour of the less socially-responsible categories of recreational drone users, who are the most likely to create threats to public safety.
This brief review of current regulatory schemes for small drones in the USA, the EU and Australia suggests that only a small proportion of the options identified in the framework are currently being applied. Moreover, it is far from clear that the regimes satisfy the criteria proposed in Table 1. The review also demonstrates that the 4-part research framework presented in this paper is sufficiently comprehensive to provide a basis for detailed analysis not only of past and current regimes, but also of variants and extensions that may be needed in the future, as accidents proliferate and public opinion demands greater interventionism.
As with all regulatory regimes, many of the measures involved fall outside the scope of the IS profession and discipline. That is of course the case with many IT applications, including those in accountancy, human resources management, manufacturing and financial services. However, a considerable number of opportunities in the drone regulatory area are specifically IS in nature. Moreover, the broader legal, industry structure and social considerations represent essential context for effective IS design.
The objective of this paper was declared as being the presentation of a framework whereby IS professionals and academics can achieve sufficient understanding of regulatory regimes, can identify opportunities for the development and deployment of RegTech, and can conceive, design and deliver appropriate technological support to relevant organisations. The framework's effectiveness in achieving that aim has been demonstrated by means of firstly a broad scan of ways in which IS can support activities in the six upper layers of the regulatory heirarchy, and secondly a more detailed consideration of one particular context within which IS practitioners and academics can make contributions to improved regulatory outcomes.
The framework comprises four views of the regulatory space, one of them concerned with the nature of regulatory schemes, another with layers of regulatory mechanisms, a third with the players involved in the processes, and the fourth with the activities that those entities engage in. Application of the framework enables a considerable number of opportunities to be identified. Appropriate regulatory design varies considerably depending on the context, and usually comprises a customised, and in many cases relatively small, sub-set of the rich suite of possibilities.
The efficacy of the framework has been demonstrated . The models have been shown to be of analytical value, and capable of enabling quite specific design options to be generated. A further important contribution is a set of criteria whereby any particular regulatory regime can be evaluated. The framework does not itself extend to the design and implementation phases of IS that perform or assist with regulatory functions. This would be inappropriate, however, because the process of converting requirements statements arising from application of the framework comprises generic activities that are already well-supported by existing theories, tools and expertise.
Regulators, regulatees and beneficaries alike can use the framework as a basis for analysing and articulating their needs, and for conducting cost/benefit/risk analyses of particular propositions. Software suppliers can evaluate opportunities for the creation of new applications and the adaptation and enhancement of existing products. At a more abstract level, the framework provides a basis for assessing existing regulatory schemes and the technological support available for them. It enables the generation of ideas for adaptations of and enhancements to existing regulatory regimes, and designs for alternative regulatory schemes and associated RegTech.
The work is a preliminary foray into a recently-defined field, however, and accordingly has many limitations. The framework was developed by applying and adapting existing regulatory theory. That body of theory is, however, very rich and dynamic. Alternative interpretations are feasible, which might call into question aspects of the framework, might suggest variations to the models, or might give rise to alternative models.
Although many of the contributions sought and delivered are in the realm of practice, the framework also has considerable implications for IS research. The framework's basis in regulatory theory requires further consideration by specialists in the economic and legal aspects of regulation, as well as by IS academics. Although it draws on theory in relevant areas external to IS, the framework is by definition pre-theoretic in nature. Progress depends on bodies of theory being harnessed and developed within the context that it provides, and empirical studies undertaken to gain insight into and refine both the theories and the framework. Beyond the limited, essentially confirmatory, study of the drone industry presented in this paper, the four models that make up the framework need to be evaluated. That requires the conduct of deep case studies of a sufficiently rich variety of industry sectors, jurisdictional contexts and regulatory regimes. The propositions relating to generic and sector-specific examples of RegTech also need to be subjected to examination. The Annexes to this paper provide a basis for this further work. The accumulation of empirical evidence will enable refinement of the propositions.
The analysis proceeded on the assumption that formal regulation continues to be relevant and feasible, at least in some contexts. That is demonstrably the case in many countries in at least a few areas, such as passenger aviation safety, financial services, and anything related to 'counter-terrorism'. On the other hand, large corporations have been increasing their scale and trans-national nature for decades. The scope for jurisdictional arbitrage has increased, as countries engage in 'regulatory competition', eagerly ratcheting down the control exercised over corporate behaviour in order to attract more economic activity (e.g. Backer 2008). Particularly since the turn of the century, new business models have been challenging existing regulatory regimes (Clemons & Madhani 2010). A further threat to formal regulation has emerged in the form of the so-called 'sharing economy' associated with the Airbnb / Uber business model. This has been accompanied by pleas for regulatory schemes to be simply abandoned in favour of a new 'innovation imperative' (e.g. Koopman et al. 2015). Meanwhile, in many countries, a significant proportion of elected representatives are subject to bribery or other means of achieving favourable treatment for corporations (Amundsen 1999), or are dependent on corporate support for their campaign finance (Lessig 2011).
In such circumstances, the enactment of formal regulation is very difficult and instead pressure is exerted for de-regulation. As a result of these factors, the extent to which individual nation-states can effectively control the behaviour of large corporations is in some doubt. A further factor in many countries is the use of excessive regulation as a means of extracting bribes from organisations that are trying to conduct even mainstream economic and social activities. This is just one of many aspects of cultural relativity that need to be taken into account when applying the framework. As further insights are accumulated, it is likely to become apparent that adaptations are needed to the framework.
The term RegTech is capable of interpretation as referring to technologies generally, whereas the analysis conducted in this paper is strongly oriented towards information technology and IS. Consideration needs to be given as to whether a broader scope is needed, encompassing engineering (e.g. construction, energy) and the sciences generally (e.g. pharmaceuticals, industrial chemicals, clinical psychology), and whether the models are applicable in such contexts or need refinement, or whether they necessitate an entirely different framework.
The RegTech notion was first applied in the financial services sector, and specifically in order to assist regulatees to achieve compliance with formal regulation. The analysis presented here has shown that such a narrow conception is unnecessarily limiting, and that much can be gained from a broader interpretation. RegTech has the capacity to benefit regulators, regulatees and beneficiaries. It can be applied to both generic business functions and industry-specific needs. It is not limited to formal regulation, but can be applied to all forms of co- and self-regulation as well, and to infrastructural regulation. The framework presented above provides a basis for contributions by IS professionals and researchers in this important area.
Abdullah N.S., Sadiq S. & Indulska M. (2010) 'Emerging Challenges in Information Systems Research for Regulatory Compliance Management' Proc. 22nd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Hammamet Tunisia, June 2010
Ahuja M.K. (2002) 'Women in the information technology profession: a literature review, synthesis and research agenda' European Journal of Information Systems 11 (2002) 20-34, at https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/5c05/af60eb00cd9364643157398a3bdd1aee2b7f.pdf
Akhigbe O., Amyot D. & Richards G. (2015). 'Information Technology Artifacts in the Regulatory Compliance of Business Processes: A Meta-Analysis' Proc. 6th International MCETECH Conference on E-Technologies, Montreal Canda, May 2015
Akhigbe O., Amyot D., Mylopoulos J. & Richards, G. (2017) 'What can Information Systems do for Regulators? A Review of the State-of-Practice in Canada' Proc. 11th IEEE International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science, Brighton UK, May 2017
Alt R., Beck R. & Smits M.T. (2018) 'FinTech and the transformation of the financial industry' Electronic Markets 28, 3 (2018) 235-243, at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12525-018-0310-9
Amundsen I. (1999) 'Political Corruption: An Introduction to the Issues' Chr. Michelsen Institute Development Studies and Human Rights Working Paper, 1999, at https://brage.bibsys.no/xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2435773/WP1999.7%20Inge-07192007_3.pdf
Anagnostopoulos I. (2018) 'Fintech and regtech: Impact on regulators and banks' Forthcoming, Journal of Economics & Business, online July 2018
ANAO (2007) 'Administering Regulation: Better Practice Guide' Australian National Audit Office, March 2007, at http://www.anao.gov.au/~/media/Uploads/Documents/administering_regulation_.pdf
ANAO (2014) 'Better practice guide: Administering Regulation: Achieving the right balance' Australian National Audit Office, June 2014, at https://www.anao.gov.au/work/better-practice-guide/administering-regulation-achieving-right-balance
APF (2013) 'Meta-Principles for Privacy Protection' Australian Privacy Foundation, March 2013, at http://www.privacy.org.au/Papers/PS-MetaP.html
Arner D.W., Barberis J. & Buckley R.P. (2015) 'The Evolution of FinTech: A New Post-Crisis Paradigm?' University of Hong Kong Faculty of Law Research Paper No. 2015/047, UNSW Law Research Paper No. 2016-62, October 2015, at https://hub.hku.hk/bitstream/10722/221450/1/Content.pdf?accept=1
Arner D.W., Barberis J. & Buckley R.P. (2016) 'FinTech, RegTech and the Reconceptualization of Financial Regulation' Northwestern Journal of International Law and Business, PrePrint of October 2016 at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2847806
Avgerou C. (2008) 'Information systems in developing countries: a critical research review' Journal of Information Technology 23 (2008) 133 - 146, at http://ai2-s2-pdfs.s3.amazonaws.com/c130/a316d37382ba89b05ffbaebfe85c0068e6ad.pdf
Ayres I. & Braithwaite J. (1992) 'Responsive Regulation: Transcending the Deregulation Debate' Oxford Univ. Press
Backer L.C. (2008) 'Multinational Corporations as Objects and Sources of Transnational Regulation' ILSA Journal of International & Comparative Law 14,2 (2008) 499-523, at http://nsuworks.nova.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1624&context=ilsajournal
Balleisen E.J. & Eisner M. (2009) 'The Promise and Pitfalls of Co-Regulation: How Governments Can Draw on Private Governance for Public Purpose' Ch. 6 in Moss D. & Cisternino J. (eds.) 'New Perspectives on Regulation' The Tobin Project, 2009, pp.127-149, at http://elearning.muhajirien.org/index.php/catalog/download/filename/New_Perspectives_Full_Text.pdf#page=127
Baxter L.G. (2016) 'Adaptive financial regulation and regtech: a concept article on realistic protection for victims of bank failures' Duke L. J. 66 (2016) 567-604, at http://scholarship.law.duke.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3873&context=dlj
von Bertalanffy L. (1940) 'Der Organismus als physikalisches System betrachtet' Die Naturwissenschaften 28 (1940) 521-53
von Bertalanffy L. (1968) 'General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications' George Braziller, 1968
Braithwaite J. (1982) `Enforced self-regulation: A new strategy for corporate crime control' Michigan Law Review 80, 7 (1982) 1466-507
Braithwaite J. (2017) 'Types of responsiveness' Chapter 7 in Drahos (2017), pp. 117-132, at http://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n2304/pdf/ch07.pdf
Brown H., Cook R. & Gabel M. (1978) 'Environmental Design Science Primer' Advocate Press, 1978
CASA (2002) 'Unmanned Aircraft and Rockets: Model Aircraft' Civil Aviation Safety Authority Advisory Circular AC 101-3(0) , July 2002, at https://www.casa.gov.au/files/101c03pdf
CASA (2016) 'Commercial unmanned flight - remotely piloted aircraft under 2kg' Civil Aviation Safety Authority, September 2016, at https://www.casa.gov.au/standard-page/commercial-unmanned-flight-remotely-piloted-aircraft-under-2kg
CASA (2017) 'Flying drones or model aircraft recreationally' Civil Aviation Safety Authority, August 2017, at https://www.casa.gov.au/modelaircraft
Clarke R. (1992) 'Practicalities of Keeping Confidential Information on a Database With Multiple Points of Access : Technological and Organisational Measures' Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, September 1992, Invited Paper for a Seminar of the Independent Commission Against Corruption of the State of N.S.W. on 'Just Trade? A Seminar on Unauthorised Release of Government Information', Sydney Opera House, 12 October 1992, at http://www.rogerclarke.com.au/DV/PaperICAC.html
Clarke R. (1995) 'A Normative Regulatory Framework for Computer Matching' Journal of Computer & Information Law XIII,4 (Summer 1995) 585-633, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/DV/MatchFrame.html#IntrCtls
Clarke R. (1999) 'Internet Privacy Concerns Confirm the Case for Intervention' Commun. ACM 42, 2 (February 1999) 60-67, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/DV/CACM99.html
Clarke R. (2001a) 'Meta-Brands' Privacy Law & Policy Reporter 7, 11 (May 2001), PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/DV/MetaBrands.html
Clarke R. (2001b) 'Towards a Taxonomy of B2B e-Commerce Schemes' Proc. 14th Int'l eCommerce Conf., Bled, Slovenia, June 2001, pp. 591-615, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/Bled01.html
Clarke R. (2013) 'Data Risks in the Cloud' Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research (JTAER) 8, 3 (December 2013) 60-74, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/II/DRC.html
Clarke R. (2014a) 'Understanding the Drone Epidemic' Computer Law & Security Review 30, 3 (June 2014) 230-246, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/SOS/Drones-E.html
Clarke R. (2014b) 'What Drones Inherit from Their Ancestors' Computer Law & Security Review 30, 3 (June 2014) 247-262, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/SOS/Drones-I.html
Clarke R. (2014c) 'The Regulation of of the Impact of Civilian Drones on Behavioural Privacy' Computer Law & Security Review 30, 3 (June 2014) 286-305, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/SOS/Drones-BP.html#RN
Clarke R. (2015) 'The Prospects of Easier Security for SMEs and Consumers' Computer Law & Security Review 31, 4 (August 2015) 538-552, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/SSACS.html
Clarke R. (2016a) 'Big Data, Big Risks' Information Systems Journal 26, 1 (January 2016) 77-90, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/BDBR.html
Clarke R. (2016b) 'Appropriate Regulatory Responses to the Drone Epidemic' Computer Law & Security Review 32, 1 (Jan-Feb 2016) 152-155, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/SOS/Drones-PAR.html
Clarke R. (2016c) 'Practicable Backup Arrangements for Small Organisations and Individuals' Australasian Journal of Information Systems, 20 (September 2016), at http://dx.doi.org/10.3127/ajis.v20i0.1250, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/PBAR.html
Clarke R. & Bennett Moses L. (2014) 'The Regulation of Civilian Drones' Impacts on Public Safety' Computer Law & Security Review 30, 3 (June 2014) 263-285, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/SOS/Drones-PS.html
Clarke R. & Jenkins M. (1993) 'The Strategic Intent of On-Line Trading Systems: A Case Study in National Livestock Marketing' Journal of Strategic Information Systems 2,1 (March 1993) 57-76, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/CALM.html
Clemons E.K. & Madhani N. (2010) 'Regulation of Digital Businesses with Natural Monopolies or Third-Party Payment Business Models: Antitrust Lessons from the Analysis of Google' J. of Mngt Infor. Syst. 27, 3 (2010) 43-80
Cleven A. & Winter R. (2009) 'Regulatory Compliance in Information Systems Research - Literature Analysis and Research Agenda' Proc. BPMD- S/EMMSAD Proceedings, 2009, pp. 174-186, Springer, 2009
Coglianese C. (2004) 'Information technology and regulatory policy: New directions for digital government research'. Social Science Computer Review, 2004, at https://sites.hks.harvard.edu/m-rcbg/Conferences/rpp_rulemaking/Coglianese_IT&RegPolicy.pdf
Cousins K. & Varshney U. (2014) 'The Regulatory Issues Affecting Mobile Financial Systems: Promises, Challenges, and a Research Agenda' Communications of the Association for Information Systems 34, 75
Daley M. & Butler B. (2018) 'Conduct risk: towards a model for assessment and remediation' Journal of Decision Systems 27 (2018), at https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/12460125.2018.1468172
Drahos P. (ed.) (2017) 'Regulatory Theory: Foundations and Applications' ANU Press, 2017. at http://press.anu.edu.au/publications/regulatory-theory/download
Drahos P. & Krygier M. (2017) 'Regulation, institutions and networks' Ch. 1 in Drahos (2017), at http://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n2304/pdf/ch01.pdf
Duncombe R. & Heeks R. (2003) 'An information systems perspective on ethical trade and self-regulation' Information Technology for Development 10 (2003) 123âÄ"138, at http://itd.ist.unomaha.edu/Archives/4.pdf
EASA (2017) 'Introduction of a regulatory framework for the operation of drones' European Aviation Safety Agency, Notice of Proposed Amendment 2017-05 (B), May 2017, at https://www.easa.europa.eu/system/files/dfu/NPA%25202017-05%2520%2528B%2529.pdf
Eggert M., Winkelmann A., Lohmann P. & Knackstedt R. (2013) 'The Regulatory Influence On Management Information Systems - A Contingency Perspective' Proc. ECIS 2013, 9
El Kharbili M. (2012) 'Business Process Regulatory Compliance Management Solution Frameworks: A Comparative Evaluation' Proc. Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Information Systems, Melbourne, 2012
ENISA (2010) 'Good Practice Guide for Incident Management' European Union Agency for Network and Information Security, December 2010, at https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/good-practice-guide-for-incident-management
EPIC (2011) 'EPIC v. FTC (Enforcement of the Google Consent Order)' Electronic Privacy Information Center, 2011, at https://epic.org/privacy/ftc/google/consent-order.html
FAA (2016) 'Final Rules on Operation and Certification of Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems' Federal Aviation Administration, June 2016
FCA (2016) 'Call for input on supporting the development and adopters of RegTech' Feedback Statement FS16/4, Financial Conduct Authority, July 2016, at https://www.fca.org.uk/publication/feedback/fs-16-04.pdf
Farbey B., Land F.F. & Targett D. (1995) 'A taxonomy of information systems applications: the benefits' evaluation ladder' European Journal of Information Systems 4, 1 (1995) 41-50
Fellmann M. & Zasada A. (2014) 'State-of-the-Art of Business Process Compliance Approaches' Proc. European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) 2014, Tel Aviv Israel, 2014
Fisher J. & Harindranath G. (2004) 'Regulation as a barrier to electronic commerce in Europe: the case of the European fund management industry' Euro. J. Info. Syst. 13, 4 (2004) 260-272
Gilad S. (2008) 'Accountability or Expectations Management? The Role of the Ombudsman in Financial Regulation' Law & Policy 30, 2 (Aril 2008) 227-253, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sharon_Gilad/publication/227742895_Accountability_or_Expectations_Management_The_Role_of_the_Ombudsman_in_Financial_Regulation/links/00b4951ad881081331000000.pdf
Gilmore W.C. (2004) 'Dirty Money: The Evolution of International Measures to Counter Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism' Council of Europe Publishing, 2004
Glick B. (2015) 'Budget 2015: First look at the policies for technology' UK ComputerWeekly, 18 Mar 2015, at http://www.computerweekly.com/news/2240242539/Budget-2015-First-look-at-the-policies-for-technology
Gomber P., Kauffman R.J., Parker C. & Weber B.W. (2018) 'On the Fintech Revolution: Interpreting the Forces of Innovation, Disruption, and Transformation in Financial Services' Journal of Management Information Systems 35, 1 (2018) 220-265
Gozman D. & Currie W. (2014) 'The role of Investment Management Systems in regulatory compliance: a Post-Financial Crisis study of displacement mechanisms' Journal of Information Technology 29, 1 (Mar 2014) 44-58
Grabowsky P. (2017) 'Meta-Regulation' Chapter 9 in Drahos (2017), pp. 149-161, at http://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n2304/pdf/ch09.pdf
Greenaway K.E., Chan Y.E. & Crossier R.E. (2015) 'Company information privacy orientation: a conceptual framework' Info Systems J 25, 6 (2015) 579-606
Gunningham N., Grabosky P, & Sinclair D. (1998) 'Smart Regulation: Designing Environmental Policy' Oxford University Press, 1998
Gunningham N. & Sinclair D. (2017) 'Smart Regulation', Chapter 8 in Drahos (2017), pp. 133-148, at http://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n2304/pdf/ch08.pdf
Gupta,A. & Lad L. (1983) `Industry self-regulation: An economic, organizational, and political analysis' The Academy of Management Review 8, 3 (1983) 416-25
Hardin G. (1968) 'The Tragedy of the Commons' Science 162 (1968) 1243-1248, at http://cescos.fau.edu/gawliklab/papers/HardinG1968.pdf
Hashmi M., Governatori G., Lam H.-P. & Wynn M.T. (2018) 'Are We Done with Business Process Compliance: State-of-the-Art and Challenges Ahead' Knowledge and Information Systems, January 2018
Henry K., Fox M.S. & Sengupta A. (2007) 'How To Build Enterprise Data Models To Achieve Compliance To Standards Or Regulatory Requirements (and share data)' Journal of the Association for Information Systems 8, 2, Article 5
Hobbs J.E. (2004) 'Information Asymmetry and the Role of Traceability Systems' Agribusiness 20, 4 (2004) 397-415, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jill_Hobbs/publication/227645596_Information_asymmetry_and_the_role_of_traceability_system/links/53cee2aa0cf2f7e53cf7e308/Information-asymmetry-and-the-role-of-traceability-system.pdf
Hosein G., Tsavios P. & Whitley E. (2003) 'Regulating Architecture and Architectures of Regulation: Contributions from Information Systems' International Review of Law, Computers and Technology 17, 1 (2003) 85-98
Hosein I. & Whitley E.A. (2002) 'The regulation of electronic commerce: learning from the UK's RIP Act' Journal of Strategic Information Systems 11, 1 (March 2002) 31-58
Huang G.K.J. & Chiang K.-H. (2017). 'RegTech Evolution: The TrustChain' Proc. ICEB 2017, 42
IIF (2015) 'RegTech: Exploring Solutions for Regulatory Challenges' Institute of International Finance', October 2015, at https://www.iif.com/topics/regtech/regtech-exploring-solutions-regulatory-challenges
IIF (2016) 'RegTech in Financial Services: Technology Solutions for Compliance and Reporting' Institute of International Finance', March 2016, at https://perma.cc/VKM6-HP8L
ISO (2006) 'Customer Satisfaction - guidelines for complaints handling' ISO 10002:2006 International Standards Organisation, 2006
Ives B., Hamilton S., & Davis G. B. (1980) 'Framework for Research in Computer-Based Management Information Systems' Management Science 26, 9 (1980) 910-934
Jansen-Vullers M.H., van Dorp C.A. & Beulens A.J.M. (2003) 'Managing traceability information in manufacture' International Journal of Information Management 23, 5 (October 2003) 395-413
King A.A. & Lennox M.J. (2000) 'Industry self-regulation without sanctions: The chemical industry's responsible care program' Academy of Management J. 43, 4 (August 2000) 698-716, at http://tuck-fac-cen.dartmouth.edu/images/uploads/faculty/andrew-king/selfreg.pdf
King W. (1978) 'Strategic Planning for Management Information Systems' MIS Quarterly 2,1 (1978) 27-37
Klapper L., Laeven L. & Rajan R. (2006) 'Entry regulation as a barrier to entrepreneurship' Journal of Financial Economics 82 (2006) 591-629, at http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.576.1585&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Knackstedt R., Eggert M., Heddier M., Chasin F. & Becker J. (2013) 'The Relationship of IS and Law - The Perspective of and Implications for IS Research' Proc. ECIS 2013, 18
Knackstedt R., Braeuer S., Heddier M. & Becker J. (2014) 'Integrating Regulatory Requirements into Information Systems Design and Implementation' Proc. ECIS 2014
Koopman C., Mitchell M. & Thierer A. (2015) 'The Sharing Economy and Consumer Protection Regulation: The Case for Policy Change' Bus. Entrepreneurship & L. 8 (2015) 529-545, at http://digitalcommons.pepperdine.edu/jbel/vol8/iss2/4
Lane M.S. & Koronios A. (2001) 'e-Pharmacy (www.epharmacy.com.au): A Successful Online Pharmacy in Australia' Proc. 14th Bled Electronic Commerce Conf., June 2001
Lessig L. (1999) 'Code and Other Laws of Cyberspace' Basic Books, 1999
Lessig L. (2011) 'Republic, Lost: How Money Corrupts Congress - and a Plan to Stop It' Twelve, 2011
Libecap G.D. (2008) 'State Regulation of Open-Access, Common-Pool Resources' Ch.21 in Ménard C. & Shirley M.M. (Eds,) 'Handbook of New Institutional Economics' , Springer, 2008
Lord N. (2017) 'The History of Data Breaches' Digital Guardian, 27 July 2017, at https://digitalguardian.com/blog/history-data-breaches
Lynch D. & Vogel D. (2001) 'The Regulation of GMOs in Europe and the United States: A Case-Study of Contemporary European Regulatory Politics' Council on Foreign Relations, April 2001, at http://www.ask-force.org/web/Regulation/Lynch-Regulation-GMOs-Europe-USA-2001.pdf
Lynes J.K. & Andrachuk M. (2008) 'Motivations for corporate social and environmental responsibility: A case study of Scandinavian Airlines' Journal of International Management 14 (2008) 377-390, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mark_Andrachuk/publication/227417810_Motivations_for_corporate_social_and_environmental_responsibility_A_case_study_of_Scandinavian_Airlines/links/5714f37708ae9bfcf4cf001c.pdf
Madani K. (2010) 'Game theory and water resources' Journal of Hydrology 381 (2010) 225-238, at http://www.academia.edu/download/33676442/GT_WR.pdf
Minor J. (2014) 'Local Government Fracking Regulations: A Colorado Case Study' Stanford Environmental L. J. 33, 1 (2014) 59-120, at http://journals.law.stanford.edu/sites/default/files/stanford-environmental-law-journal-selj/print/2014/01/h_minor_article_-_web_0.pdf
Mlcakova A. & Whitley E.A. (2004) 'Configuring peer-to-peer software: an empirical study of how users react to the regulatory features of software' European Journal of Information Systems 13, 2 (2004) 95-102
Moores T.T. & Dhillon G. (2003) 'Do privacy seals in e-commerce really work?' Communications of the ACM 46, 12 (December 2003) 265-271
Moyano J.P. & Ross O. (2017) 'KYC Optimization Using Distributed Ledger Technology'. Business & Information Systems Engineering 59, 6 (2017) 411-423
Neo B.S. (1992) 'The implementation of an electronic market for pig trading in Singapore' Journal of Strategic Information Systems 1, 5 (December 1992) 278-288
Ngai E.W.T., Hu Y., Wong Y.H., Chen Y. & Sun X. (2011) 'The application of data mining techniques in financial fraud detection: A classification framework and an academic review of literature' Decision Support Systems 50, 3 (February 2011) 559-569
Parker C. (2002) 'The Open Corporation: Effective Self-regulation and Democracy' Cambridge University Press, 2002
Parker C. (2007) 'Meta-Regulation: Legal Accountability for Corporate Social Responsibility?' in McBarnet D, Voiculescu A & Campbell T (eds), The New Corporate Accountability: Corporate Social Responsibility and the Law, 2007
PC (2006) 'Rethinking Regulation' Report of the Taskforce on Reducing Regulatory Burdens on Business, Productivity Commission, January 2006, t http://www.pc.gov.au/research/supporting/regulation-taskforce/report/regulation-taskforce2.pdf
Rai A., Arikan I., Pye J. & Tiwana A. (2015) 'Fit and Misfit of Plural Sourcing Strategies and IT-Enabled Process Integration Capabilities: Consequences of Firm Performance in the U.S. Electric Utility Industry' MIS Quarterly 39, 4 (2015) 865-885
RBA (2014) 'The Regulatory Response to the Global Financial Crisis' Chapter 3 of Submission to the Financial System Inquiry, March 2014, at http://www.rba.gov.au/publications/submissions/financial-sector/financial-system-inquiry-2014-03/regulatory-response-to-the-global-financial-crisis.html
Reimers K., Li M., Xie B. & Guo X, (2015) 'How do industry-wide information infrastructures emerge? A life cycle approach' Information Systems Journal 24, 5 (September 2014) 375-424
Rukanova B., Van Stijn E., Henriksen H.Z., Baida Z. & Tan Y.-H. (2009) 'Understanding the influence of multiple levels of governments on the development of inter-organizational systems' European Journal of Information Systems 18, 5 (Oct 2009) 387-408
Sadiq S. & Governatori G. (2015). 'Managing regulatory compliance in business processes' Handbook on Business Process Management 2, Springer, 2015, at http://www.governatori.net/papers/2013/handbookBPM.pdf
Schultz M. (2013) 'Towards an Empirically Grounded Conceptual Model for Business Process Compliance' Proc. International Conference on Conceptual Modeling, 2013, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Martin_Schultz4/publication/263543342_Towards_an_Empirically_Grounded_Conceptual_Model_for_Business_Process_Compliance/links/55d6e40a08aeb38e8a84217d.pdf
Sethi S.P. & Emelianova O. (2006) 'A failed strategy of using voluntary codes of conduct by the global mining industry' Corporate Governance 6, 3 (2006) 226-238, at https://19-659-fall-2011.wiki.uml.edu/file/view/A+Failed+Strategy+of+Using+Voluntary+Codes+of+Conduct+by+the+Global+Mining+Industry.pdf/248416241/A+Failed+Strategy+of+Using+Voluntary+Codes+of+Conduct+by+the+Global+Mining+Industry.pdf
Shapiro S.A. (2012) 'Blowout: Legal Legacy of the Deepwater Horizon Catastrophe:The Complexity of Regulatory Capture: Diagnosis, Causality, and Remediation' Roger Williams Uni. L. Rev. 17, 1 (Winter 2012) 221-257, at http://docs.rwu.edu/rwu_LR/vol17/iss1/11
Smith S., Winchester D., Bunker D. & Jamieson R. (2010) 'Circuits of Power : A Study of Mandated Compliance to an Information Systems Security De Jure Standard in a Government Organization' MIS Quarterly 34, 3 (September 2010) 463-486
Stiglitz J. (2008) 'Government Failure vs. Market Failure' Principles of Regulation - Working Paper #144, Initiative for Policy Dialogue, February 2008, at http://policydialogue.org/publications/working_papers/government_failure_vs_market_failure/
Tang Z., Yu J. & Smith M.D. (2008) 'Gaining Trust Through Online Privacy Protection: Self-Regulation, Mandatory Standards, or Caveat Emptor' J. of Mngt Infor. Syst. 24, 4 (2008) 153-173
Treleaven P. (2015) 'Financial regulation of FinTech' EY Journal of Financial Perspectives 3, 3 (Winter 2015), at https://fsinsights.ey.com/dam/jcr:f4626c4c-e1b7-4e59-a910-319fd19ab5a8/financial-regulation.pdf
Tsatsou P., Elaluf-Calderwood S. & Liebenau J. (2010) 'Towards a taxonomy for regulatory issues in a digital business ecosystem in the EU' Journal of Information Technology 25, 3 (Sep 2010) 288-307
UKGOS (2015) 'FinTech futures: the UK as a world leader in financial technologies' UK Government Office for Science, March 2015, at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/fintech-blackett-review
Wall J.D., Lowry P.B. & Barlow J.B. (2016) 'Organizational Violations of Externally Governed Privacy and Security Rules: Explaining and Predicting Selective Violations under Conditions of Strain and Excess' J. Ass. Infor. Syst. 17, 1 (2016)
Wand Y. & Weber R. (2002) 'Research Commentary: Information Systems and Conceptual Modeling-- A Research Agenda' Information Systems Research 13, 4 (December 2002) 363-376, at http://www.cs.northwestern.edu/~paritosh/papers/sketch-to-models/wand-weber-information-systems-and-conceptual-modeling-2002.pdf
Watson R.T., Boudreau M.-T. & Chen A.J. (2010) 'Information Systems and Environmentally Sustainable Development: Energy Informatics and New Directions for the IS Community' MIS Quarterly 34 1 (March 2010). 23-38
Wiener N. (1948) 'Cybernetics, or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine' MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1948, 1961
Williams T.A. (1994) 'Government regulation through voluntary cooperation: the strategic impact of information technology Journal of Strategic Information Systems 3, 2 (June 1994) 107-122
Williams T.A. (1996) 'Government regulation through voluntary cooperation: a follow-up study of the strategic impact of information technology' Journal of Strategic Information Systems 5, 2 (June 1996) 149-156
Williamson O.E. (1979) 'Transaction-cost economics: the governance of contractual relations' Journal of Law and Economics 22, 2 (October 1979) 233-261
Winn J.K. (2017) 'What Impact Will 'RegTech' Have on the Legal Profession?' Seminar, Soochow University School of Law, Taipei, Taiwan, 7 January 2017
Xu H., Teo H.H., Tan B.C.Y. & Agarwal R. (2012) 'Research Note--Effects of Individual Self-Protection, Industry Self-Regulation, and Government Regulation on Privacy Concerns: A Study of Location-Based Services' Information Systems Research 23, 4 (2012) 1342-1363
Zagaris B, (2004) 'The Merging of the Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financial Enforcement Regimes after September 11, 2001' BerkeleyJ. Int'lLaw 22, 1 (2004) 123-158, at http://scholarship.law.berkeley.edu/bjil/vol22/iss1/6
Major Group
('Division') | Sector ('Group' and 'Class') | Regulatory
Considerations |
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | Growing of Controlled Crops (e.g. Poppies for Opium, Tobacco, Marijuana) | Public health |
| Hunting, trapping and related service activities | Protected species, animal welfare | |
| Fishing | Sustainability, species protection | |
| Aquaculture | Water pollution, species protection | |
| Mining and quarrying | Mining of coal and lignite | Air pollution, groundwater pollution |
| Extraction of crude petroleum and natural gas | Air pollution, groundwater pollution, public safety | |
| Support activities for petroleum and natural gas extraction | Air pollution, groundwater pollution, public safety | |
| Mining and quarrying of controlled materials (e.g. asbestos, mercury, titanium) | Public safety, strategic resources | |
| Manufacturing but also Importation | Processing and preserving of meat | Public health, tracking of individual items |
| Dairy products | Public health | |
| Alcoholic beverages | Public health, taxation | |
| Tobacco products | Public health, taxation | |
| Tanning and dressing of leather | Groundwater pollution, public health | |
| Paper and paper products | Groundwater pollution, public health | |
| Reproduction of recorded media | Copyright breach | |
| Refined petroleum products | Air pollution, groundwater pollution, public safety | |
| Fissile material | Air, ground and groundwater pollution, public safety, control of explosive materials, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Fertilizers and nitrogen compounds | Public safety, control of explosive materials, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Pesticides and other agrochemical products | Public safety, control of explosive materials | |
| Dangerous chemicals (e.g. ammonia, propellants, explosives) | Public safety, control of explosive materials, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Pharmaceuticals | Public safety | |
| Weapons and ammunition | Public safety, control of explosive materials, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Irradiation equipment | Public health and safety | |
| Medical and dental instruments and supplies | Public health and safety | |
| Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply | Electric power generation, transmission and distribution | Public health and safety |
| Manufacture of gas; distribution of gaseous fuels through mains | Public health and safety | |
| Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities | Collection of hazardous waste | Groundwater pollution, public health and safety |
| Treatment and disposal of hazardous waste | Air, water, ground and groundwater pollution, public health and safety | |
| Construction | Development application | Air, water, ground and groundwater pollution, species protection, public health and safety |
| Demolition and site preparation | Air, water, ground and groundwater pollution, public health and safety | |
| Electrical installation | Public health and safety | |
| Wholesale and retail trade ... | Motor vehicles | Consumer protection, public safety, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime |
| Food, alcoholic beverages and tobacco | Public health, taxation | |
| Solid, liquid and gaseous fuels and related products | Public safety | |
| Pharmaceutical and medical goods | Public health and safety, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Weapons and ammunition | Public safety, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Devices for interception, jamming, encryption and decryption | Protection of telecommunications | |
| Dangerous goods (e.g. explosives) | Public safety, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Transportation and storage | Freight transport by road | Public safety |
| Passenger air transport | Public safety | |
| Freight air transport | Public safety | |
| Accommodation and food service activities | Accommodation | Public health and safety |
| Restaurants and mobile food service activities | Public health and safety | |
| Beverage serving activities | Public health and safety | |
| Information and communication | Radio broadcasting | Protection of telecommunications |
| Television programming and broadcasting activities | Protection of telecommunications | |
| Wireless telecommunications activities | Protection of telecommunications | |
| Satellite telecommunications activities | Protection of telecommunications | |
| Financial and insurance activities | Financial Services (e.g. banks, credit unions) | Protection of critical infrastructure, protection against financial and taxation fraud, investigation of money laundering |
| Financial Exchanges | Investor protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Trusts, funds and similar financial entities | Protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Credit granting | Consumer protection | |
| Pawn shops | Criminal investigation, location of individual items | |
| Life insurance | Consumer protection | |
| Health insurance | Consumer protection, public health | |
| Non-Life insurance | Consumer protection | |
| Pension funding | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Activities of insurance agents and brokers | Consumer protection | |
| Activities of financial planners | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Fund management activities | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Real estate activities | Consumer protection | |
| Professional, scientific and technical activities | Legal activities | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud |
| Accounting, bookkeeping and auditing activities; tax consultancy | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Company directorship activities | Investor protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Architectural and engineering activities and related technical consultancy | Public safety | |
| Veterinary activities | Animal welfare | |
| Administrative and support service activities | Travel agency activities | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud |
| Tour operator activities | Consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud | |
| Private security activities | Public safety | |
| Investigation activities | Consumer protection | |
| Activities of collection agencies incl. debt collectors, and credit bureaus | Consumer protection | |
| Public administration and defence; compulsory social security | ||
| Education | Child day-care activities | Protection of children |
| Pre-primary and primary education | Protection of children | |
| Human health and social work activities | Hospital activities | Public health and safety |
| Medical and dental practice activities | Public health and safety | |
| Pharmaceutical supplies | Public health and safety, tracking of individual items, prevention of crime | |
| Residential care activities | Public health and safety | |
| Social work activities | Public health and safety | |
| Migration consultants | Consumer protection, protection against fraud | |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | Gambling and betting activities | Public health, consumer protection, protection against financial and taxation fraud |
| Activities of sports clubs | Protection of children | |
| Activities of amusement parks and theme parks | Public safety | |
| Other service activities | Funeral and related activities | Consumer protection |
| Activities of households as employers; undifferentiated goods; own use production | ||
| Activities of extraterritorial organizations and bodies |
Regulator | Regulatee | Beneficiary | |
Formal Regulation
Meta- and Co-Regulation
Industry Self-Regulation
Organisational Self-Regulation | Management systems for own-motion investigations
Management systems for complaints investigations
Registration / Licensing Systems
Case Management Support Systems Subsidy and Levy Management Systems | Exception detection mechanisms
Systems for measurement, recording, analysis, response and
reporting
Product registration systems
Incident management systems
Complaints management systems Data management systems (anti-discrimination and positive discrimination
measures; OH&S/WHS; energy efficiency measures)
Automated statistical reporting systems
Compliance management systems Compliance audit support systems | Policy database systems
Case evaluation wizards
Support systems for preparation and submission of complaints Case management systems |
Infrastructural Regulation | Direct access to organisational transaction systems Auto-reporting from organisational systems | Access control, audit trailing, automated monitoring of audit trails
Data integrity safeguards
Detection of exception conditions and unusual occurrences in real-time
Detection of exception condictions and unusual occurrences through
retrospective analysis
Auto-adjustments of parameters in response to input/process/output
measures
Auto-deployment of countermeasures Auto-suspension of activities | |
| Natural Regulation | Exercise of countervailing power by
those affected by an initiative
Activities by competitors
Reputational effects Cost/benefit trade-offs | ||
A preliminary version of the layer model in this paper was presented as part of an address on 'Biometrics as RegTech?' at the 10th Workshop on the Social Implications of National Security (SINS17) in Sydney, on 9 August 2017. Valuable comments were received from Ross Buckley, Peter Drahos, Graham Greenleaf, Neil Gunningham and Michael Walters, but responsibility for all aspects of the paper rests with the author.
Roger Clarke is Principal of Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, Canberra. He is also a Visiting Professor in Cyberspace Law & Policy at the University of N.S.W., and a Visiting Professor in the Research School of Computer Science at the Australian National University.
| Personalia |
Photographs Presentations Videos |
Access Statistics |
 |
The content and infrastructure for these community service pages are provided by Roger Clarke through his consultancy company, Xamax. From the site's beginnings in August 1994 until February 2009, the infrastructure was provided by the Australian National University. During that time, the site accumulated close to 30 million hits. It passed 65 million in early 2021. Sponsored by the Gallery, Bunhybee Grasslands, the extended Clarke Family, Knights of the Spatchcock and their drummer |
Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd ACN: 002 360 456 78 Sidaway St, Chapman ACT 2611 AUSTRALIA Tel: +61 2 6288 6916 |
Created: 31 July 2017 - Last Amended: 14 November 2018 by Roger Clarke - Site Last Verified: 15 February 2009
This document is at www.rogerclarke.com/EC/RTF.html
Mail to Webmaster - © Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 1995-2022 - Privacy Policy